Alcoholism: Difference between revisions
imported>Michael J. Formica (Organizational structure) |
imported>Meg Taylor No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
'''Alcoholism''' is a chronic condition, the development and presentation of which is influenced by [[genetic]], [[psychosocial]], and [[environment|environmental]] factors. As a [[disease]] process, it is often progressive, and sometimes [[death|fatal]]. | {{Image|Mri alcohol.gif|right|350px|Images of a 61-year-old healthy man (upper images) and a 60-year-old alcoholic man (lower images). Note on the MRI the thinner corpus callosum displaced upward by enlarged ventricles and, on the DTI, less well delineated white matter tracts in the alcoholic man compared with the healthy man.}} | ||
'''Alcoholism''' is a chronic condition, the development and presentation of which is influenced by [[genetic]], [[psychosocial]], and [[environment|environmental]] factors. As a [[disease]] process, it is often progressive, and sometimes [[death|fatal]]. Alcoholism is typically characterized by impaired [[impulse control]], preoccupation with [[alcohol (drug)|alcohol]], continued use of alcohol despite adverse consequences, and a generalized distortion in thinking. While the condition itself is considered chronic, the symptom profile may present either continuously or periodically." <ref name="title">{{cite web |url=http://www.nlm.nih.gov/cgi/mesh/2007/MB_cgi?term=Alcoholism |title=Alcoholism |author=National Library of Medicine |accessdate=2007-12-06 |format= |work=}}</ref> | |||
==Etiology / cause== | |||
Alcoholism is "probably a multifactorial, genetically influenced disorder" and [[twin study|twin studies]] show a "55% or higher concordance rate in monozygotic twins with only a 28% rate for like-sex dizygotic twins."<ref>Alcohol Dependence. ({{OMIM|103780}})</ref> | |||
==Alcoholic styles== | ==Alcoholic styles== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 21: | ||
===Post-recovery=== | ===Post-recovery=== | ||
==Diagnosis== | |||
A [[systematic review]] concluded "full AUDIT may be superior to the AUDIT-C."<ref name="pmid19075207">{{cite journal |author=Kriston L, Hölzel L, Weiser AK, Berner MM, Härter M |title=Meta-analysis: are 3 questions enough to detect unhealthy alcohol use? |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=149 |issue=12 |pages=879–88 |year=2008 |month=December |pmid=19075207 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=19075207 |issn=}}</ref> | |||
One question, "'How many times in the past year have you had X or more drinks in a day?', where X is 5 for men and 4 for women, and a response of >1 is considered positive" has accuracy of:<ref>{{Cite journal | |||
| doi = 10.1007/s11606-009-0928-6 | |||
| volume = 24 | |||
| issue = 7 | |||
| pages = 783-788 | |||
| last = Smith | |||
| first = Peter | |||
| coauthors = Susan Schmidt, Donald Allensworth-Davies, Richard Saitz | |||
| title = Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test | |||
| journal = Journal of General Internal Medicine | |||
| accessdate = 2009-06-16 | |||
| date = 2009-07-01|pmid=19247718 | |||
| url = http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11606-009-0928-6 | |||
}}</ref> | |||
* [[Sensitivity and specificity|Sensitivity]] 82% | |||
* [[Sensitivity and specificity|Specificity]] 79% | |||
===Hair analysis=== | |||
Hair analysis can detect alcohol consumption by measuring fatty acid ethyl esters and ethyl glucuronide that are metabolites of [[ethanol]].<ref name="pmid16624267">{{cite journal |author=Pragst F, Balikova MA |title=State of the art in hair analysis for detection of drug and alcohol abuse |journal=Clin. Chim. Acta |volume=370 |issue=1-2 |pages=17–49 |year=2006 |month=August |pmid=16624267 |doi=10.1016/j.cca.2006.02.019 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0009-8981(06)00122-7 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18367991">{{cite journal |author=Pragst F, Yegles M |title=Determination of fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) and ethyl glucuronide (EtG) in hair: a promising way for retrospective detection of alcohol abuse during pregnancy? |journal=Ther Drug Monit |volume=30 |issue=2 |pages=255–63 |year=2008 |month=April |pmid=18367991 |doi=10.1097/FTD.0b013e318167d602 |url=http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?an=00007691-200804000-00021 |issn=}}</ref> | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
===Medications=== | ===Medications=== | ||
====Acamprosate ==== | |||
"[[Acamprosate]] appears to be an effective and safe treatment strategy for supporting continuous abstinence after detoxification in alcohol dependent patients" according to the [http://cochrane.org Cochrane Collaboration].<ref name="pmid20824837">{{cite journal| author=Rösner S, Hackl-Herrwerth A, Leucht S, Lehert P, Vecchi S, Soyka M| title=Acamprosate for alcohol dependence. | journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev | year= 2010 | volume= 9 | issue= | pages= CD004332 | pmid=20824837 | doi=10.1002/14651858.CD004332.pub2 }} </ref> In this review, the [[number needed to treat]] was about 9 patients. | |||
====Baclofen==== | ====Baclofen==== | ||
Baclofen is | Baclofen is a selective GABA B-receptor agonist that in a single trial of patients with alcoholic cirrhosis improved abstinence rates (71% versus 29%) over three months.<ref name="pmidpending">2007. [http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140673607618145/abstract Lancet]</ref> | ||
====Disulfiram==== | ====Disulfiram==== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 57: | ||
====Topiramate==== | ====Topiramate==== | ||
[[Randomized controlled trial]]s of volunteers showed benefit from [[topiramate]].<ref name="pmid18541827">{{cite journal| author=Johnson BA, Rosenthal N, Capece JA, Wiegand F, Mao L, Beyers K et al.| title=Improvement of physical health and quality of life of alcohol-dependent individuals with topiramate treatment: US multisite randomized controlled trial. | journal=Arch Intern Med | year= 2008 | volume= 168 | issue= 11 | pages= 1188-99 | pmid=18541827 | doi=10.1001/archinte.168.11.1188 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18541827 }} </ref><ref name="pmid17925516">{{cite journal| author=Johnson BA, Rosenthal N, Capece JA, Wiegand F, Mao L, Beyers K et al.| title=Topiramate for treating alcohol dependence: a randomized controlled trial. | journal=JAMA | year= 2007 | volume= 298 | issue= 14 | pages= 1641-51 | pmid=17925516 | doi=10.1001/jama.298.14.1641 | pmc= | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=17925516 }} </ref> | |||
====Naltrexone==== | ====Naltrexone==== | ||
| Line 33: | Line 63: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
[[ | [[Alcohol (drug)]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
Revision as of 06:11, 18 October 2013
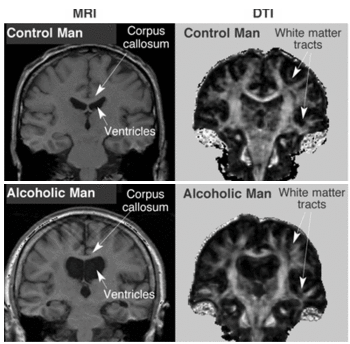
Images of a 61-year-old healthy man (upper images) and a 60-year-old alcoholic man (lower images). Note on the MRI the thinner corpus callosum displaced upward by enlarged ventricles and, on the DTI, less well delineated white matter tracts in the alcoholic man compared with the healthy man.
Alcoholism is a chronic condition, the development and presentation of which is influenced by genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors. As a disease process, it is often progressive, and sometimes fatal. Alcoholism is typically characterized by impaired impulse control, preoccupation with alcohol, continued use of alcohol despite adverse consequences, and a generalized distortion in thinking. While the condition itself is considered chronic, the symptom profile may present either continuously or periodically." [1]
Etiology / cause
Alcoholism is "probably a multifactorial, genetically influenced disorder" and twin studies show a "55% or higher concordance rate in monozygotic twins with only a 28% rate for like-sex dizygotic twins."[2]
Alcoholic styles
Chronic drinking
Maintenance drinking
Binge drinking
Blackout drinking
Recovery styles
The 'dry drunk'
In recovery
Post-recovery
Diagnosis
A systematic review concluded "full AUDIT may be superior to the AUDIT-C."[3]
One question, "'How many times in the past year have you had X or more drinks in a day?', where X is 5 for men and 4 for women, and a response of >1 is considered positive" has accuracy of:[4]
- Sensitivity 82%
- Specificity 79%
Hair analysis
Hair analysis can detect alcohol consumption by measuring fatty acid ethyl esters and ethyl glucuronide that are metabolites of ethanol.[5][6]
Treatment
Medications
Acamprosate
"Acamprosate appears to be an effective and safe treatment strategy for supporting continuous abstinence after detoxification in alcohol dependent patients" according to the Cochrane Collaboration.[7] In this review, the number needed to treat was about 9 patients.
Baclofen
Baclofen is a selective GABA B-receptor agonist that in a single trial of patients with alcoholic cirrhosis improved abstinence rates (71% versus 29%) over three months.[8]
Disulfiram
A randomized controlled trial showed benefit from disulfiram [9]
Topiramate
Randomized controlled trials of volunteers showed benefit from topiramate.[10][11]
Naltrexone
Randomized controlled trials show conflicting benefit from naltrexone with benefit among recent abstainers[12] and no benefit from chronic users[13].
See also
References
- ↑ National Library of Medicine. Alcoholism. Retrieved on 2007-12-06.
- ↑ Alcohol Dependence. (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. MIM Number: 103780. World Wide Web URL: http://omim.org/.)
- ↑ Kriston L, Hölzel L, Weiser AK, Berner MM, Härter M (December 2008). "Meta-analysis: are 3 questions enough to detect unhealthy alcohol use?". Ann. Intern. Med. 149 (12): 879–88. PMID 19075207. [e]
- ↑ Smith, Peter; Susan Schmidt, Donald Allensworth-Davies, Richard Saitz (2009-07-01). "Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test". Journal of General Internal Medicine 24 (7): 783-788. DOI:10.1007/s11606-009-0928-6. PMID 19247718. Retrieved on 2009-06-16. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Pragst F, Balikova MA (August 2006). "State of the art in hair analysis for detection of drug and alcohol abuse". Clin. Chim. Acta 370 (1-2): 17–49. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2006.02.019. PMID 16624267. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Pragst F, Yegles M (April 2008). "Determination of fatty acid ethyl esters (FAEE) and ethyl glucuronide (EtG) in hair: a promising way for retrospective detection of alcohol abuse during pregnancy?". Ther Drug Monit 30 (2): 255–63. DOI:10.1097/FTD.0b013e318167d602. PMID 18367991. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Rösner S, Hackl-Herrwerth A, Leucht S, Lehert P, Vecchi S, Soyka M (2010). "Acamprosate for alcohol dependence.". Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9: CD004332. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD004332.pub2. PMID 20824837. Research Blogging.
- ↑ 2007. Lancet
- ↑ Fuller RK, Branchey L, Brightwell DR, et al (1986). "Disulfiram treatment of alcoholism. A Veterans Administration cooperative study". JAMA 256 (11): 1449–55. PMID 3528541. [e]
- ↑ Johnson BA, Rosenthal N, Capece JA, Wiegand F, Mao L, Beyers K et al. (2008). "Improvement of physical health and quality of life of alcohol-dependent individuals with topiramate treatment: US multisite randomized controlled trial.". Arch Intern Med 168 (11): 1188-99. DOI:10.1001/archinte.168.11.1188. PMID 18541827. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Johnson BA, Rosenthal N, Capece JA, Wiegand F, Mao L, Beyers K et al. (2007). "Topiramate for treating alcohol dependence: a randomized controlled trial.". JAMA 298 (14): 1641-51. DOI:10.1001/jama.298.14.1641. PMID 17925516. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Anton RF, O'Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, et al (2006). "Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE study: a randomized controlled trial". JAMA 295 (17): 2003–17. DOI:10.1001/jama.295.17.2003. PMID 16670409. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Krystal JH, Cramer JA, Krol WF, Kirk GF, Rosenheck RA (2001). "Naltrexone in the treatment of alcohol dependence". N. Engl. J. Med. 345 (24): 1734–9. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa011127. PMID 11742047. Research Blogging.